HVAC System: Enhancing Comfort and Efficiency in Indoor Environments.
HVAC SYSTEM, an acronym for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning, is a vital technology and system that regulates the indoor environment in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Its primary purpose is to ensure thermal comfort and maintain a healthy and suitable indoor environment for occupants. By controlling temperature, humidity, and air quality, HVAC systems create a comfortable and productive space, regardless of external weather conditions. This article will delve into the various components, functions, and benefits of HVAC systems, highlighting their significance in enhancing comfort and energy efficiency in indoor settings.
I. Heating Component :
The heating component of an HVAC system is responsible for maintaining warmth during cold weather conditions. It employs different heating sources such as furnaces, boilers, or heat pumps to generate heat. These systems utilize various fuel sources, including gas, oil, electricity, or geothermal energy. The generated heat is then distributed throughout the building using ductwork, radiators, or radiant floor systems. By raising the indoor temperature to the desired level, the heating component ensures thermal comfort, allowing occupants to withstand chilly climates with ease.
II. Ventilation Component
The ventilation aspect of HVAC systems focuses on air exchange, indoor air quality, and moisture control. Ventilation involves the exchange of stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air to maintain optimal air quality. Proper ventilation reduces the concentration of airborne pollutants, allergens, odors, and excess moisture, promoting a healthier environment. Ventilation systems comprise fans, ductwork, and air vents, which facilitate the movement and circulation of air throughout the building. Additionally, advanced ventilation systems incorporate heat recovery mechanisms to minimize energy loss during the air exchange process.
III. Air Conditioning Component
The air conditioning component is crucial for maintaining a cool and comfortable indoor environment during hot weather. It employs compressors, condensers, and evaporators to remove heat from the indoor air. By extracting heat and moisture, the system cools the air, ensuring pleasant temperatures. The cooled air is then distributed through ductwork and air vents, evenly cooling various zones or rooms within the building. Air conditioning systems use different configurations, such as central air conditioning, split systems, or ductless mini-split systems, to cater to specific building requirements.
IV. Control and Automation
HVAC systems incorporate sophisticated controls and automation technologies to optimize performance and energy efficiency. Programmable thermostats and advanced control panels allow occupants to set desired temperature levels, schedule heating or cooling cycles, and adjust ventilation rates. Moreover, sensors placed throughout the building monitor temperature, humidity, and air quality, enabling the system to make real-time adjustments based on environmental conditions. Integration with smart home automation systems further enhances control and allows remote monitoring and management of HVAC systems.
V. Benefits of HVAC Systems
HVAC systems offer numerous benefits, making them indispensable in modern buildings. Firstly, they provide comfortable indoor environments by maintaining the desired temperature, humidity, and air quality levels. This contributes to occupant satisfaction, productivity, and overall well-being. Secondly, HVAC systems improve indoor air quality by removing pollutants, allergens, and excess moisture, promoting a healthier living or working space. Additionally, these systems enhance energy efficiency through advanced technologies like energy-efficient compressors, variable speed drives, and heat recovery systems, reducing energy consumption and lowering utility costs. HVAC systems also contribute to sustainability efforts by incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar or geothermal energy. Lastly, they provide precise control and automation options, allowing customized settings and optimizing performance based on specific building requirements.
In conclusion, HVAC systems play a pivotal role in ensuring comfortable and healthy indoor environments. By integrating heating, ventilation, and air conditioning components, these systems create optimal thermal conditions, maintain air quality, and control humidity levels. With advanced control and automation features, HVAC systems offer flexibility, convenience, and energy efficiency. The benefits of HVAC systems extend beyond comfort, contributing to occupant well-being, productivity, and environmental sustainability. As technology continues to evolve, HVAC systems will continue to advance, further enhancing the indoor environment and revolutionizing the way we experience and interact with our built spaces.
How does it work?
HVAC systems work through a series of processes involving heating, ventilation, and air conditioning to regulate the indoor environment.
Here is a detailed explanation of how HVAC systems function:
- Heating: When the desired temperature is set, the heating component of the HVAC system is activated. The heating source, such as a furnace, boiler, or heat pump, generates heat by burning fuel (e.g., gas or oil), using electricity, or utilizing geothermal energy. The heat is then transferred to the air or water within the system.
- Air Intake: The system draws in air from the surrounding environment through return air vents. This air may be a combination of fresh outdoor air and recirculated indoor air.
- Conditioning: If heating is required, the air passes through the heating component. The heat generated by the furnace, boiler, or heat pump is transferred to the air, raising its temperature. If cooling is needed, the air goes through the air conditioning component.
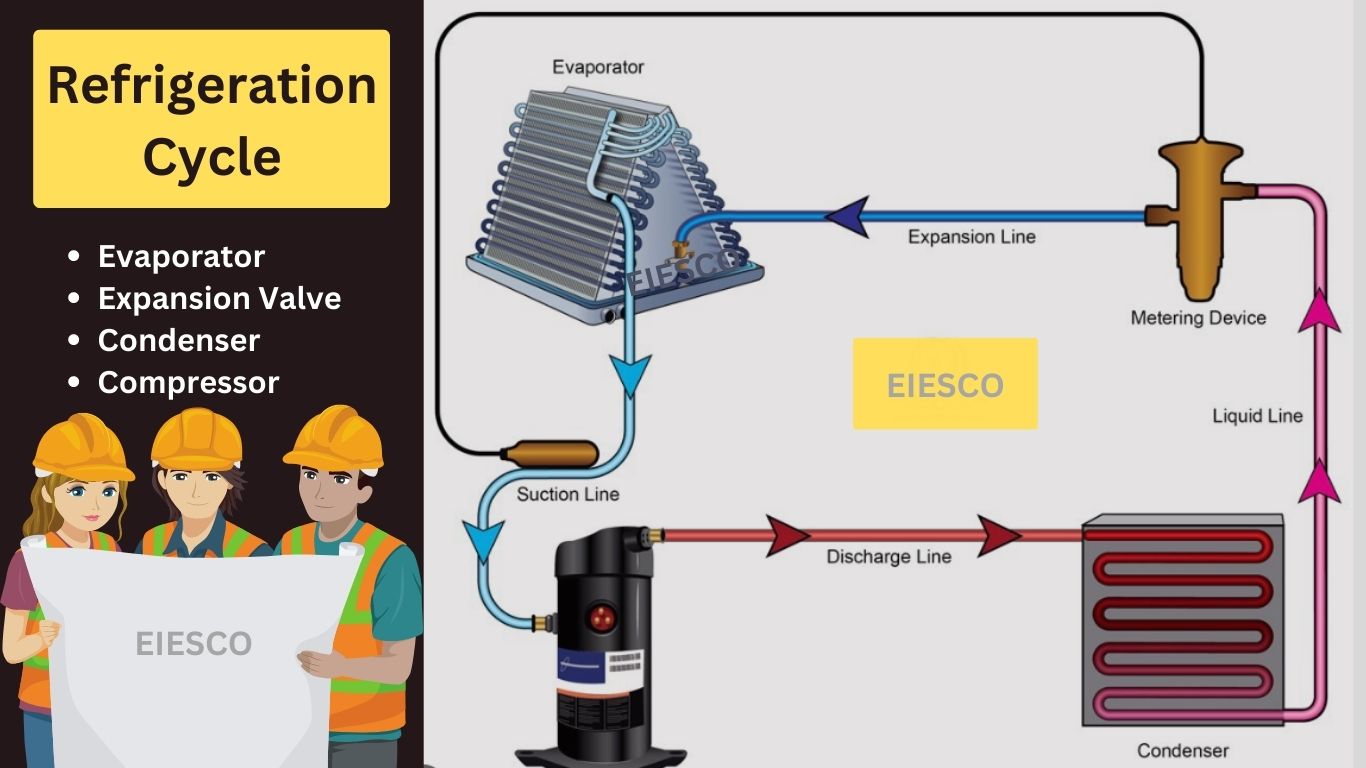
- Air Conditioning: The air conditioning component consists of a compressor, condenser, and evaporator. In cooling mode, the compressor compresses refrigerant gas, increasing its temperature and pressure. The high-pressure, high-temperature gas flows through the condenser, where it releases heat to the surroundings and condenses into a high-pressure liquid. The liquid refrigerant then passes through an expansion valve or metering device, which reduces its pressure and temperature. As a result, it evaporates into a low-pressure gas and absorbs heat from the air passing through the evaporator coil. This process cools the air, reducing its temperature.
- Air Distribution: The conditioned air is distributed throughout the building using a network of ducts, vents, and registers. The ductwork carries the heated or cooled air to different rooms or zones. In some systems, the air is circulated through a series of pipes in radiant floor systems or through radiators to transfer heat.
- Ventilation: Fresh air is introduced into the HVAC system to maintain indoor air quality. It can be achieved through mechanical ventilation systems, which use fans to draw in outdoor air, or through a combination of mechanical and natural ventilation. The ventilation component helps remove stale air, odors, and airborne pollutants, ensuring a healthy indoor environment. In some cases, heat recovery ventilation systems are employed to recover heat from the exhaust air and pre-condition the incoming fresh air, improving energy efficiency.
- Air Exhaust: Exhaust vents and fans are used to expel stale air, excess moisture, and pollutants from the building. This helps to maintain air quality and prevent the buildup of contaminants.
- Control and Monitoring: The HVAC system is equipped with controls and sensors to monitor and regulate the indoor environment. Thermostats or control panels allow occupants to set the desired temperature, and the system adjusts heating, cooling, and ventilation accordingly. Sensors located throughout the building measure temperature, humidity, and air quality parameters, providing feedback to the system for automatic adjustments. Advanced HVAC systems may also integrate with smart home automation systems, allowing remote control and monitoring.
By combining these processes, HVAC systems create a comfortable indoor environment by regulating temperature, humidity, and air quality. The system continuously operates to maintain the desired conditions, ensuring occupant comfort and well-being.




